DDNS.org Troubleshooting
What can go wrong?
The basic configuration has 3 steps:
- Configure modem for dyndns update
- Configure modem for port forwarding
- Use the hostname to access from remote
The connection problem may be due to one or more of these steps. In this section we see how you can find exactly what's wrong and how to fix it.
{info}The tests included in this page allow us to find the cause of 99% of connection problems of our users and fix them. We hope this list can help you too.
Check if the connection has a Public IPv4
First thing first. Your Internet connection must have a Public IPv4 (dynamic) which means that the operator is not using NAT.
Check the IP assigned by the Internet operator on the WAN and compare it with the Private IP table.
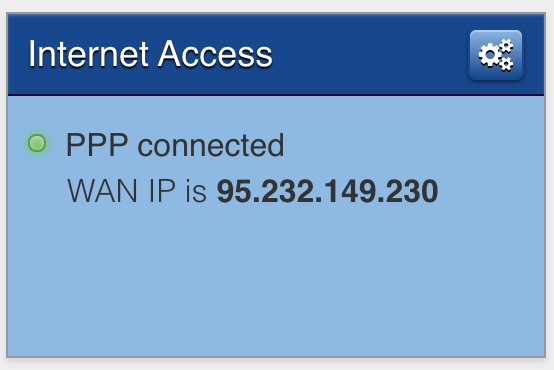
If the IP belongs to the private IP table there is a good chance that the network has a NAT. If in doubt, check with your operator if your line uses NAT and if it is possible to DENAT the line.
These are the IP classes usually used for private networks, you can find the full reserved IP address table here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4#Special-use_addresses
| From | to | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 | Private Network |
| 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 | Private Network |
| 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 | Private Network |
| 100.64.0.0 | 100.127.255.255 | Private Network |
If the operator uses NAT on your line, it is not possible to reach your connection from remote, because the NAT uses the same public IP for thousand of users.
This is an issue that DDNS cannot solve. You should use a VPN or a P2P service to reach devices in your LAN.
{info} If the IP on the WAN of your modem is not in the previous table, hence is a Public IPv4, you can proceed with the following check to troubleshoot the problem.
Check if the ports are open on the Internet
This check is to verify that the ports are indeed open on the Internet.
Use the YouGetSignal site to perform this check. This site allows you to directly control the opening of the ports on the IP. DYNAMIC DNS and hostname are not used in this test.
Remember that you can test from remote only the TCP ports. UDP ports cannot be checked from remote.
If the ports are not open on the IP, and you are sure that you line is not blocked from operator, then the issue is between the modem and the device.
Common causes and solutions for closed ports are:
- Modem Firewall is blocking all remote connection
- Check the modem Firewall and set it at a lower level
- Device is not listening on the port forwarded
- Check that the device is on
- Check that you can connect in LAN to the device on same ports that you opened.
- Reboot the device to be sure that is not blocked by other connections.
- Modem Port forwarding configuration is not correct
- Check the correctness of each forwarding rule in the modem. Pay attention to enter the correct IP of the device to be reached in the LAN (usually 192.168.1.xxx).
- Check that you are forwarding the correct protocol. In doubt forward both TCP and UDP.
- If the modem requires, in the forwarding rule, an external IP then the enter 0.0.0.0/0 or leave it blank if possible.
- Device Firewall is blocking connection from remote
- Check that the firewall of the device allows connection from the external world (0.0.0.0/0) for your ports. This is particular true for PCs.
- Try to lower or disable the device firewall for test. Disabling a firewall is NEVER a good idea! Do it only for test.
{info} If the ports are open from the Internet, then the modem port forwarding is set up correctly. You can proceed to the next checks.
Check if the modem updates the hostname
If the previous tests are ok, then you can check if the modem updates correctly the DDNS.
1 - Switch off the modem and wait a minute so the IP on the line changes.
2 - Switch on the modem and wait a couple of minutes to be sure that the modem has the time to send an update to the hostname.
3 - So, after a coffee, visit the page: https://checkip.dyndns.it from a browser connected to the modem (ie with your smartphone connected in WiFi to the modem) and note your current IP.
4 - Visit your DDNS dashboard https://ddns.org/dashboard, and note the hostname IP
If the two IP are equal then the modem correctly updates the dyndns and you can proceed to the next check.
If the two IP are different then the modem is not updating the hostname and the problem resides in modem dyndns configuration. Access the administration interface of the modem and check the dyndns configuration page to see if there is any error. Many time is just the user or the password entered with wrong caps.
{info} If the modem updates correctly the hostname, then the dyndns service is operating correctly. The Hostname point to your conenction IP.
App Configuration
Last thing to check if the ports are open, the DDNS is updated and points to your connection, is the client configuration.
The client is the software that you use to connect to your device. It can be, for example, an Internet Browser or a mobile App.
Pay attention to enter the hostname as the address of the device and, if necessary, indicate the port that you have opened.
For example, if you
- use an Internet browser to connect to the device
- your host name is myexamplehost.fixip.org
- you opened the port 8080
then you should use the address http://myexamplehost.fixip.org:8080
in the form
<http or https> :// <the hostname> : <the port>Still not working?
If, after successfully running the tests given here, you are still unable to connect with your device, try contacting support
using the form https://ddns.org/dashboard/contact-form.
Be sure to explain in detail your issue, and, if possible, attach
a screen dump of your configuration.